
Fluoropolymer is a super excellent material!
Fluoropolymer was discovered by Dr. Planket at Dupon Company in the USA in 1938. The sample he discovered was polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the very first fluoropolymer.
After his discovery, so many researches were done for fluoropolymer besides PTFE. Due to its special functions and excellent characteristics, a variety of fluoropolymer (including PFA and FEP) was synthesized. Nowadays, fluoropolymer has become a material indispensable in a wide variety of fields such as medical, chemical, semiconductor, and automobile as well as aerospace and submarine cables in addition to household products.
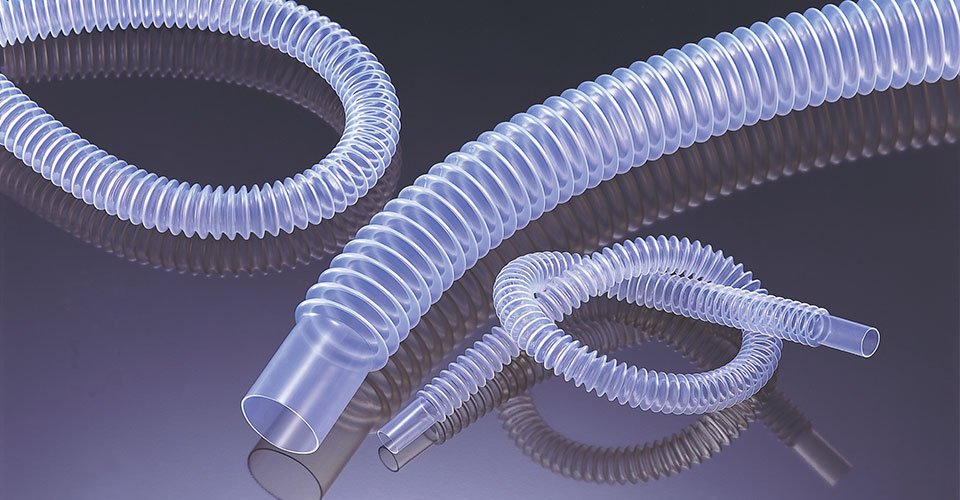
Fluoropolymer tubing is tubing made from fluoropolymer that has special functions and excellent characteristics.
There are many types of fluoropolymer tubing such as flexible tubing used for piping, heat shrink tubing used for protecting the target material inside the tubing, extruded tubing, as well as slim and fat, or ultra-thin and thick tubing. Applications are in wide variety from aerospace to undersea technology.
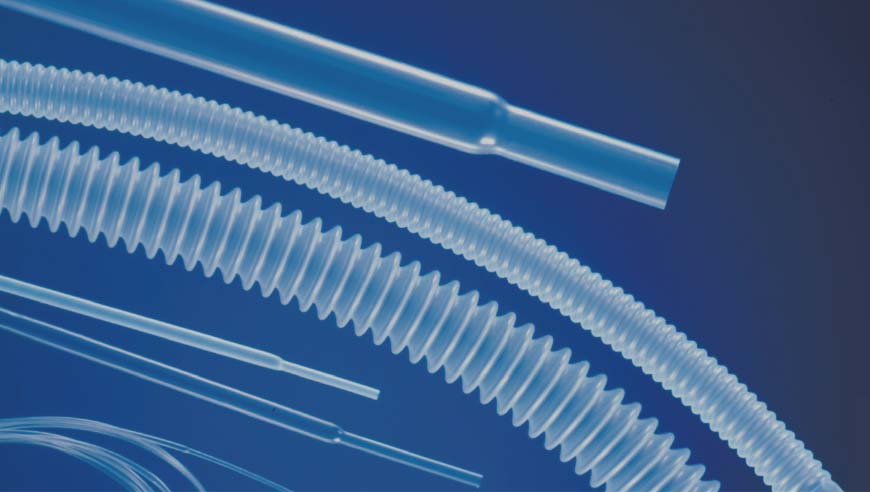
The flexible tubing has a flexibility in bending radius that can be used for piping.
Heat shrink tubing and extruded tubing can protect and alter the surface characteristics of the inside target material. These tubes have variety of forms and sizes that can be adjusted for the inside material.
Among high-functional resin, fluoropolymer has rather higher working temperatures and thus has less thermal decomposition and is strong even in the high temperature environment.
*Highest working temperature (no load): SMT/SST200°C, WTF230°C, PFA/TFE/TFE4X260°C
Fluoropolymer is resistant to chemicals with high corrosiveness (excluding some chemicals). Especially, TFE, EPA and FEP have high chemical resistance under high temperature and there are few chemicals that corrode ETFE and PVDF.
* The chemical resistance is affected by conditions and environment (temperature, pressure, etc.). Before using, we recommend you to test at your actual conditions and environment.
Fluoropolymer has stable electric characteristics in high temperature and high frequency environments compared to other insulators. Especially, dissipation factor and dielectric constant for TFE are stable up to 10,000MHz in temperatures between -40 deg.C and 240 deg.C.
WTF has double fluoropolymer constructions with TFE and FEP. The inner FEP melts when heated and the outer TFE shrinks to wrap and seal the material inside the tubing.
Fluoropolymer has a characteristic of non-combustibility with low smoke when burnt. In addition, TFE doesn’t exhibit smoke.
No matter how viscous the fluid is, or no matter if the fluid is adhesive, they never clog the fluoropolymer tubing. In addition, if they stick to the tube, they can be easily washed out.
Fluoropolymer tubing has low friction factor among other high functional resin and has excellent smoothness.
* Static friction factor: TFE 0.02, PFA 0.05, FEP 0.05
Fluoropolymer does not deteriorate over years under the direct sun light.
* When tested under strong ultra-violet ray for one year, qualities of TFE and FEP tubing did not change.
Fluoropolymer material is not made of plasticizer or flame-retardant agent. In addition, it is chemically inactive thus it rarely contaminates other materials.
Heat shrink and extruded tubing adds insulation, non-viscosity, and smoothness characteristics to the target material only by covering it. Furthermore, it protects the target material from the external environment with chemical resistance, moisture-proof, and non-contamination, and supports the target material easily. It is used for tying electric wires and harnesses and for insulation in a variety of applications including medical, aerospace, electric devices, vehicles, and home electronics.
Flexible tubing is used as a piping material in the manufacturing equipment of semiconductor, liquid crystal, and quarts, and MA, measurement, and laboratory appliances.
Sensor / heat-resistant cover, tools for piping
Thermistor / harness / bush cable
Magnetic head / roll / power supply harness
Power cable / optical cable / submarine cable / transmission antenna / radar / fuel cell, etc.
Artificial satellite / shuttle / airplane etc.
Catheter / testing equipment / analytical equipment
Conveying and kneading roller / clothes hanger / temperature detector / heat exchanger, etc.
Motor / compensating lead / resistor / isolator, etc.
Heater and thermistor for rice cooker, electric pot, iron
Wide range of applications including, various kinds of rollers for paper making / heat-resistant or insulator of electronics and electric device